- 2. c#基础
2. c#基础
2.1. c#方法参数
c#方法的参数一共有四种:
- 值参数:参数传递的是副本
- 引用参数:参数传递的是变量的引用。
- 方法定义:修饰符 返回值 方法名(
ref参数类型 形参名) - 方法调用:方法名(
ref实参名)
- 方法定义:修饰符 返回值 方法名(
- 输出参数:和引用参数类似,但方法内部任何的执行路径必须对输出参数赋值。
- 方法定义:修饰符 返回值 方法名(
out参数类型 形参名) - 方法调用:方法名(
out实参名)
- 方法定义:修饰符 返回值 方法名(
- 可变参数(参数数组):可以传递任意个数参数,会被封装到参数数组中
- 方法定义:修饰符 返回值 方法名(
params参数类型[] 形参名) - 方法调用:方法名(
arg1[,arg2,...]);
- 方法定义:修饰符 返回值 方法名(
using System;
namespace var_method_param
{
class Point
{
int x;
int y;
public void Print()
{
Console.WriteLine("({0},{1})", x, y);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var point = new Point();
//类的字段默认是private访问级别
//point.x = 3;
point.Print();
Console.WriteLine(Sum(5, 15));
int a = 11, b = 22;
Console.WriteLine("交换两个变量的值:");
Console.WriteLine("交换前:a={0},b={1}", a, b);
Swap(ref a, ref b);
Console.WriteLine("交换前:a={0},b={1}", a, b);
Console.WriteLine("-----------out参数---------");
int outP;
OutParam(3, out outP);
Console.WriteLine("outP:"+outP);
Console.WriteLine("-----------可变参数(参数数组)---------");
Print(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Print(3, 4, 11);
}
/*
* c#参数类型:
* 1.值类型
* 2.引用类型
* 3.传出类型
* 4.可变参数
*
*
*/
/// <summary>
/// 值参数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="b"></param>
/// <returns>两数之和</returns>
static int Sum(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
/// <summary>
/// 引用参数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="b"></param>
static void Swap(ref int a, ref int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
/// <summary>
/// out参数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="iParam"></param>
/// <param name="outParam"></param>
static void OutParam(int iParam, out int outParam)
{
outParam = iParam * 2;
}
/// <summary>
/// 可变参数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="args"></param>
static void Print(params int[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < args.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(args[i]);
if (i < args.Length-1)
{
Console.Write(",");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
}
另外,c#的方法参数可以指定默认值,在调用方法时对于指定了默认值的参数可以不用传递,如下所示:
static int GetOffset(int pageSize = 10, int page = 1)
{
return (page - 1) * pageSize;
}
2.2. c#类
2.2.1. 修饰符
- const:常量修饰符
- readonly: 类似于常量修饰符,一旦值被设定就不能改变,但和const也有区别: const字段或变量只能在声明语句中初始化,值必须在编译期确定,没有内存空间;readonly字段有内存空间,可以在声明语句或者constructor中初始化。
2.2.2. 类成员
c#的类有9种成员:
2.2.2.1. 字段
- 实例字段:类中的变量,每个实例有自己的字段
- 类字段(静态字段):类的所有实例共享的变量
2.2.2.2. 常量
const修饰的变量,对所有实例可见,和static关键字冲突。只能通过类名.常量访问,且常量的值必须在编译期确定,常量在编译器被替换,没有自己的存储空间。2.2.2.3. 方法
2.2.2.4. 属性
属性代表类的实例或类中的数据项的成员。 属性的特征:
- 是命名的类成员
- 有类型
- 可以被赋值和读取
属性和字段的区别:
+ 属性是函数成员
+ 属性不为数据存储分配内存
+ 属性执行代码
属性的本质是一组两个匹配的、成为**访问器**的方法:
+ set访问器为属性赋值
+ get访问器从属性获取值
- 属性声明和访问器
set访问器性质:
- 拥有一个单独的、隐式的值,名称为value,和属性的类型相同
- 拥有一个返回类型void
get访问器性质:
- 参数为void
- 拥有一个返回值,和属性类型相同
声明一个属性:
[修饰符] 类型 属性名{
set{
一些代码
}
get{
一些代码
return 返回值;
}
}
由于属性没有存储空间,常常和字段关联使用,且通常的命名规范是:字段使用Camel命名风格,即首字母小写,其他所有单词首字母大写;属性使用Pascal命名风格,所有单词首字母大写。
- 只读和只写属性 通过只实现set或者get访问器来实现只写或只读
- 自动生成属性
c#允许只声明属性不声明其关联的后备字段,编译器会自动创建隐藏的字段,并且自动挂接到set和get访问器上。自动实现属性的要点:
- 不声明后备字段,编译器根据属性的类型自动创建
- 访问器set和get不能提供方法体,只写简单的分号
- 静态属性 跟静态字段一样,必须使用类名访问。
2.2.2.5. 构造函数(constructor)
类实例化时执行的函数 #### 2.2.2.6. 析构函数(destructor)
类被销毁之前执行的函数,一般用来清理或释放**非托管资源**,非托管资源是指通过Win32 API获取的文件句柄或非托管内存块,使用.NET是无法获得它们的,所以如果只是使用了.net类,就不需要编写destructor函数 #### 2.2.2.7. 运算符
2.2.2.8. 索引
2.2.2.9. 事件
2.2.3. partial类和partial方法
c#允许将一个class分成多个partial class声明,同时允许class的方法在不同的partial class中声明和实现,这种声明和实现分开的方法用partial修饰。
partial方法的性质如下:
- 返回值必须是void
- 方法签名不能有访问修饰符,这使得partial方法默认是隐式私有的。
- partial方法必须有声明,实现可以有可以没有,如果没有实现,编译器把方法的声明和任何对方法的调用部分都移除。
示例:
partial class PClass
{
//方法声明
partial void M1();
}
partial class PClass
{
//方法实现
partial void M1()
{
Console.WriteLine("partial method...");
}
public int Add(params int[] nums)
{
M1();
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i < nums.Length;i++)
{
sum += nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
2.2.4. 继承
c#所有的类都继承自基类object。 C#实现继承的语法:
class DerivedCalss:BaseClass{
...
}
2.2.4.1. 字段覆盖和方法覆盖
在派生类中对字段和方法使用new关键字修饰实现覆盖基类的成员和方法
using System;
namespace test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dog d = new Dog();
Animal a = d;
a.Eat();
d.Eat();
}
class Animal
{
public void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("动物吃东西.");
}
}
class Dog : Animal
{
new public void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("狗吃骨头.");
}
}
}
}
输出:
动物吃东西.
狗吃骨头.
2.2.4.2. virtual方法和override方法
对于使用new修饰的方法,如果使用基类的引用,那么调用的还是基类的方法,如果想要使用基类的引用调用派生类的方法,可以对基类方法使用virtual修饰,派生类的方法用override修饰。
性质如下:
- virtual方法和override方法必须具有相同的访问级别
- 不能对static方法使用override
- 对于方法、属性、索引器和成员类型事件,都可以使用virtual和override
示例:
using System;
namespace test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dog d = new Dog();
Animal a = d;
a.Eat();
d.Eat();
}
class Animal
{
virtual public void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("动物吃东西.");
}
}
class Dog : Animal
{
public override void Eat()
{
Console.WriteLine("狗吃骨头.");
}
}
}
}
输出:
狗吃骨头.
狗吃骨头.
2.2.5. 嵌套类
C#中的class内部可以定义class,称为嵌套类,嵌套类作为外部类的成员,跟普通成员一样,有5种访问级别:public、protected、private、internal或protected internal,默认的访问级别是private
2.3. C#运算符
2.3.1. 运算符重载
c#允许自定义运算符如何操作自定义的类型。
using System;
namespace operators
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
LimitedInt a = new LimitedInt();
LimitedInt b = new LimitedInt();
a.TheValue = 11;
b.TheValue = 22;
LimitedInt c = -a;
LimitedInt d = a + b;
Console.WriteLine("c:{0}", c.TheValue);
Console.WriteLine("d:{0}", d.TheValue);
Console.WriteLine("(a+b)的值:{0}",(a + b).TheValue);
a.TheValue = 300;
Console.WriteLine(a.TheValue);
}
}
class LimitedInt
{
const int MaxValue = 100;
const int MinValue = 0;
int _theValue = 0;
public int TheValue
{
get
{
return _theValue;
}
set
{
if (value < MinValue)
{
_theValue = 0;
}
else
{
_theValue=value > MaxValue ? MaxValue : value;
}
}
}
public static LimitedInt operator -(LimitedInt x)
{
LimitedInt li=new LimitedInt();
li.TheValue = 0;
return li;
}
public static LimitedInt operator +(LimitedInt a,LimitedInt b)
{
LimitedInt li = new LimitedInt();
li.TheValue = a.TheValue + b.TheValue;
return li;
}
}
}
结果:
Hello World!
c:0
d:33
(a+b)的值:33
100
2.4. 语句
- 表达式语句
- 控制流语句
- 条件:if-else、switch-case
- 循环:for、while、do-while、
- 跳转:break、continue、goto
-
using语句(语法糖) using语句用来隐式关闭资源,资源是指一个实现了
System.IDisposable接口的类或者结构,using语句功能跟Java中的try-with-resources语句相似。示例:
//using语句 string path="Lincoln.txt"; using (TextWriter tw = File.CreateText(path)) { tw.WriteLine("Four score and seven years ago,..."); tw.WriteLine("HelloWorld"); tw.WriteLine("The END"); } using(TextReader tr = File.OpenText(path)) { Console.WriteLine("从文件{0}中读取到下面的内容:", path); string line; while ((line = tr.ReadLine()) != null) { Console.WriteLine(line); } } - checked和unchecked语句
- foreach语句
- try、throw、finally
- yield
2.5. 结构体(struct)
struct是自定义的数据类型,和class相似,可以有数据成员和函数成员,但和class有如下的区别:
- struct是值类型,内存在栈上分配;class是引用类型,内存在堆上分配
- struct是隐式密封(sealed)的,不能被派生
示例:
using System;
namespace Struct
{
class Program
{
//结构体
struct Point
{
public int X;
public int Y;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
Point pa, pb, pc;
pa.X = 10; pa.Y = 10;
pb.X = 20; pb.Y = 20;
pc.X = pa.X + pb.X; pc.Y = pa.Y + pb.Y;
Console.WriteLine(pa.X);
Point tempP = pc;
Console.WriteLine("tempP:({0},{1})", tempP.X, tempP.Y);
tempP.X = -1;
Console.WriteLine("tempP:({0},{1})", tempP.X, tempP.Y);
Console.WriteLine("pc:({0},{1})", pc.X, pc.Y);
}
}
}
2.5.1. struct的成员
2.5.1.1. 函数
- strcut可以有构造函数(包括静态构造函数),不能有析构函数
- c#为struct隐式创建了无参构造函数,不能删除和手动定义。
- 在创建strcut实例时,如果要使用构造函数,必须和创建class实例一样使用
new关键字,即使struct不是在堆中分配内存;如果不使用new创建实例,有如下限制:- 字段在使用前必须显式赋值
- 任何函数成员被调用前要保证所有字段已经赋值
- 静态构造函数用于初始化静态字段,在下面的情况之前会被调用:
- 调用显示声明的构造函数
- 引用结构的静态成员
2.5.1.2. 字段
在struct中,实例字段声明时不能初始化,要么在构造函数中初始化,要么显式赋值。
2.6. 数组
C#中的数组都是继承自System.Array
C#的一维数组的使用和Java类似,多维数组的语法稍有不同,下面是一个C#中使用二维数组的示例:
using System;
namespace testArray
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
int[,] map = new int[3, 3] {
{1,2,3 },
{4,5,6 },
{7,8,9 }
};
for (int i = 0; i < map.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < map.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write("{0}\t", map[i, j]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
2.6.1. foreach遍历数组
//foreach遍历
Console.WriteLine("foreach遍历数组:");
int total = 0;
foreach(var n in map)
{
total += n;
Console.WriteLine("当前元素:{0},total:{1}",n,total);
}
运行结果:
foreach遍历数组:
当前元素:1,total:1
当前元素:2,total:3
当前元素:3,total:6
当前元素:4,total:10
当前元素:5,total:15
当前元素:6,total:21
当前元素:7,total:28
当前元素:8,total:36
当前元素:9,total:45
2.7. 委托
委托相当于函数/方法的指针,可以在运行时决定执行哪些方法(一个委托可以执行多个方法)。
示例:
using System;
namespace testDelegate
{
class Program
{
//声明委托
delegate void MyDel(int value);
void PrintLow(int value)
{
Console.WriteLine("Low value:{0}", value);
}
void PrintHigh(int value)
{
Console.WriteLine("High value:{0}", value);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program p = new Program();
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
MyDel del;
//生成0-99之间的随机数
Random random = new Random();
int randomValue = random.Next(99);
del = randomValue > 50 ? new MyDel(p.PrintHigh) : new MyDel(p.PrintLow);
del(randomValue);
//组合委托
Console.WriteLine("组合委托:");
MyDel del2;
//委托初始化的快捷语法,相当于del2=new MyDel(p.Method1)
del2 = p.Method1;
del2(10);
//组合委托的语法,相当于del执行时Method1和Method2都会执行一次
del2 += p.Method2;
del2(20);
//从委托移除方法
del2 = del2 - p.Method1;
del2(30);
}
void Method1(int v)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1:" + v);
}
void Method2(int v)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method2:" + v);
}
}
}
运行结果:
Hello World!
Low value:16
组合委托:
Method1:10
Method1:20
Method2:20
Method2:30
委托保存的方法可以是静态方法,也可以是实例方法,只要委托和方法的返回值类型和签名(包括ref、out修饰符)一致
2.7.1. 委托的相关运算
-
组合委托
+运算符用来组合多个委托MyDel del1=...,del2=...; MyDel del3=del1+del2;del3相当于del1和del2的方法列表的和,del3执行一次,del1和del2包括的所有方法都会执行一次。
- 委托添加方法
+=运算符用来给委托添加方法,前提是委托的引用已经初始化。MyDel del=M1; del+=M2; - 委托删除方法
-=运算符用来删除委托中的某个方法,前提是委托的引用已经初始化。MyDel del=M1; del+=M2;del+=M3; del-=M1; //最终del=M2+M3 //注意下面的情况: MyDel del=M1; del-=M1; //此时del是null,如果执行del()会抛出空指针异常2.7.2. 带有返回值的委托
如果委托有返回值且委托包含了多个方法,那么委托的返回值是最后一个方法的返回值。
namespace testDelegate
{
//委托是类不是方法,所以可以直接定义在namespace下
delegate int MyDel();
class Class1
{
public int M1()
{
return 10;
}
public int M2()
{
return 20;
}
}
}
//测试
Class1 c1=new Class1();
MyDel del1;
MyDel del2;
del1 = c1.M1;
del1 += c1.M
del2 = c1.M2;
del2 += c1.M
Console.WriteLine("del1()={0}", del1());
Console.WriteLine("del2()={0}", del2());
结果:
del1()=20
del2()=10
2.7.3. 带有引用参数的委托
当委托参数使用引用时,引用会依次传给下一个方法。
2.7.4. 匿名方法
匿名方法(anonymous method)是指初始化委托时内联的方法。 如果某些代码只会在一个地方调用那么就没有必要声明成一个单独的方法,可以使用匿名方法。
MyDel del = delegate ()
{
Console.WriteLine("匿名方法");
};
del();
下面这种情况可以省略匿名方法的圆括号:
- 委托的参数不包含out参数
- 匿名方法不使用参数
2.7.4.1. 匿名方法的变量作用域
和委托方法不同,匿名方法可以访问方法作用域之外的变量和环境。
int outVariable = 10;
MyDel del = delegate
{
Console.WriteLine("访问到外部变量:" + outVariable);
};
del();
对于块之外的代码访问不到块之内的变量:
//块之外的代码访问不到
{
int outVariable2 = 20;
MyDel del2 = delegate
{
Console.WriteLine("访问到外部变量:" + outVariable2);
};
del2();
}
//下面的代码访问不到outVariable2
//Console.WriteLine("访问到外部变量:" + outVariable2);
2.7.4.2. Lamda表达式
Lamda表达式是匿名方法的变种,但比匿名方法简洁。
MyDel del = (int n) =>
{
return n * 2;
};
Console.WriteLine(del(10));
Lamda表达式可以更进一步简略:
- 如果只有一个参数,圆括号可以省略;
- 参数类型可以省略(隐式类型),但如果参数有ref和out修饰符,则不能省略类型关键字
- 如果方法体只有一条返回语句,可以省略大括号和return关键字。
MyDel del = x => x / 2; Console.WriteLine(del(10));//5
2.8. 事件
2.8.1. 相关概念
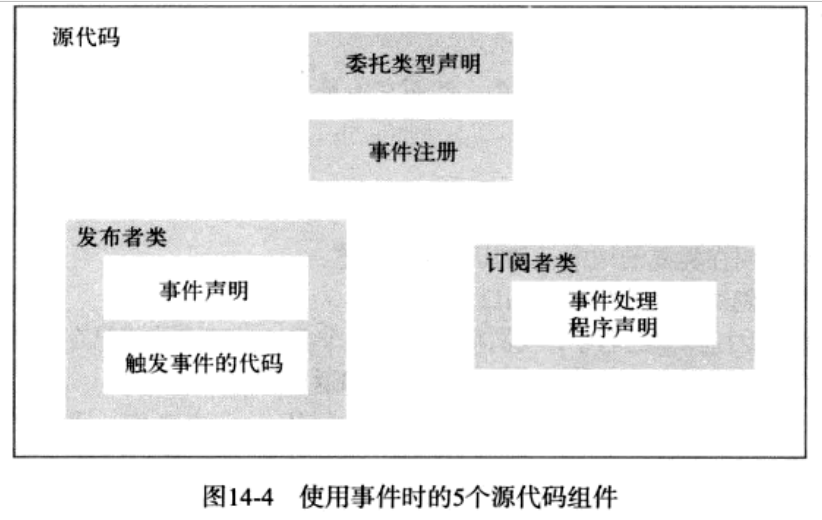
publisher:事件发布者,发布某个事件的类或结构,其他类可以在事件发生时得到通知 subscriber:事件订阅者,注册并在事件发生时得到通知的类或结构 event handler:订阅者注册到事件中的方法,发布者发布事件时执行 raise event:触发(invoke/fire)事件的行为,当事件触发时,所有注册到它的方法都会依次执行。
2.8.2. 使用事件的源代码组件概览
c#的事件依赖于委托。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace testEvent
{
//声明一个委托
delegate void Handler();
/// <summary>
/// publisher
/// </summary>
///
class Incrementer
{
//event关键字限制委托变量只能进行+=和-=运算
public event Handler CountedADozen;
public void DoCount()
{
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++)
{
if (i % 12 == 0 && CountedADozen != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}%12==0", i);
CountedADozen();
}
}
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace testEvent
{
/// <summary>
/// subscriber
/// </summary>
class Dozens
{
public int DozensCount
{ get; private set; }
public Dozens(Incrementer incrementer)
{
DozensCount = 0;
//订阅事件
incrementer.CountedADozen += IncrementDozensCount;
}
void IncrementDozensCount()
{
DozensCount++;
}
}
}
namespace testEvent
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Incrementer incrementer = new Incrementer();
Dozens dozensCounter = new Dozens(incrementer);
incrementer.DoCount();
Console.WriteLine("Numbers of dozens count:{0}",dozensCounter.DozensCount);
}
}
}
运行结果:
12%12==0
24%12==0
36%12==0
48%12==0
60%12==0
72%12==0
84%12==0
96%12==0
Numbers of dozens count:8
2.8.3. C#标准事件用法
在System命名空间下有一个EventHandler是标准的委托类型。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace testEvent_standard
{
/// <summary>
/// 自定义EventArgs
/// </summary>
class IncrementEventArgs:EventArgs
{
public int IterationCount { get; set; }
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace testEvent_standard
{
class Incrementer
{
//System.EventHandler
//public delegate void EventHandler(object sender,EventArgs e)
public event EventHandler<IncrementEventArgs> CountedADozen;
public void DoCount()
{
//传递事件参数
IncrementEventArgs args = new IncrementEventArgs();
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++)
{
if (i % 12 == 0 && CountedADozen != null)
{
args.IterationCount = i;
CountedADozen(this, args);
}
}
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace testEvent_standard
{
class Dozens
{
//声明一个DozensCount属性
public int DozensCount { get; private set; }
public Dozens(Incrementer incrementer)
{
DozensCount = 0;
incrementer.CountedADozen += IncrementDozensCount;
}
void IncrementDozensCount(object source,IncrementEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Incremented at interation: {0} in {1}", e.IterationCount, source.ToString());
DozensCount++;
}
}
}
namespace testEvent_standard
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
Incrementer incrementer = new Incrementer();
Dozens dozens = new Dozens(incrementer);
incrementer.DoCount();
Console.WriteLine("{0}", dozens.DozensCount);
}
}
}
2.8.4. 移除事件处理程序
使用-=运算符移除事件
2.9. interface
2.9.1. 性质
interface中不能声明:
- 数据成员
- 静态成员
inteface声明只能包含如下类型的非静态成员函数的声明:
- 方法
- 属性
- 事件
- 索引器 且这些成员函数不能有任何的实现。
2.9.2. 显示的成员实现
显示的接口成员实现是指在方法实现时限定接口名,调用时通过对应的接口调用。
class MyClass2 : I1, I2
{
void I1.PrintOut(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("interface 1:{0}",s);
void I2.PrintOut(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("interface 2:{0}", s)
}
}
结果:
interface 1:hello
interface 2:hello
2.10. C#类型转换
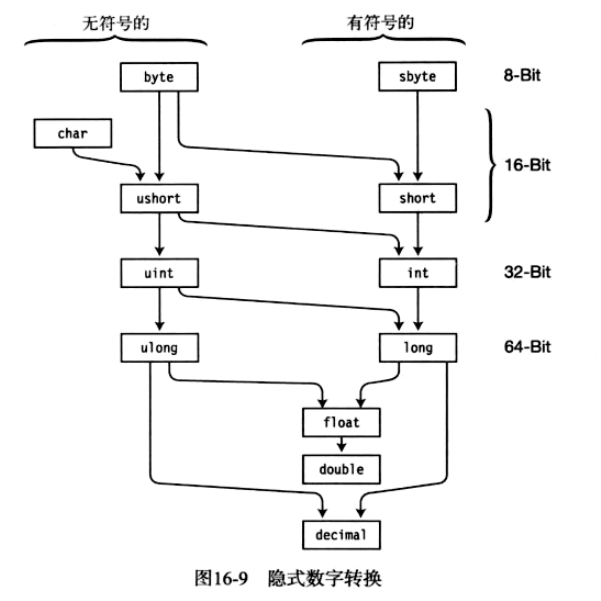
2.10.1. 数值类型转换
2.10.1.1. 溢出检测
2.10.1.1.1. checked运算符
c#提供checked(表达式)和unchenked(表达式)实现数值转换时的溢出,如果使用checked对语句进行检测,在发生数据溢出时会抛出OverflowException
如下面的代码在运行时会抛出System.OverflowException
//checked和unchecked检测溢出
byte sb;
ushort sh = 2000;
sb = checked((byte))sh
Console.WriteLine(sb);
2.10.1.1.2. checked语句块
checked语句的功能和checked表达式一样,但检测的是多个语句。
2.10.2. 引用类型转换
引用类型的对象由引用和数据组成,引用包含的信息是指向的对象的类型。
引用转换:引用转换接收源引用并返回一个指向堆中同一位置的引用,但把引用标记为其他的数据类型。
2.10.2.1. 隐式引用转换
引用也有隐式转换,且隐式转换发生在以下情况:
- 任何引用类型可以隐式转换成object类型
- 引用可以隐式转换成:
- 继承链中的任何一个类型
- 实现的任何接口
2.10.2.2. 显示引用转换
显示的引用转换一般发生在以下情况:
- 从object到其他类型的转换
- 从基类类型的引用到其派生类的转换
但是显示引用转换不总是正常,如果实际的对象不能转换成目标类型,会抛出运行时异常,显示的引用转换在下面的情况有效:
- 显示引用没有必要,比如从派生类到基类的显示引用转换。
- 源引用是null
- 源引用指向的实际数据可以被安全地隐式转换
2.10.2.3. 装箱和拆箱
包括值类型在内的所有c#类型都是派生自object类型,然而,值类型是一种轻量高效的类型,因为默认情况下在堆上不包括它们的对象组件。
2.10.2.3.1. 拆箱
如果需要值类型的对象组件,可以使用装箱(boxing),装箱是一种隐式转换。
//装箱
int a = 10;
object o =
Console.WriteLine(o);
o = 20;
Console.WriteLine(o);
Console.WriteLine(a);
装箱是创建值类型的副本。
2.10.2.3.2. 拆箱
拆箱(unboxing)是把装箱后的对象转换为值类型的过程。
object o1 = 100;
int unbox = (int)o1;
Console.WriteLine("{0}", unbox);
2.10.3. 用户自定义类型转换
在C#中,可以为类和strcut自定义类型转换,包括隐式转换和显示转换。
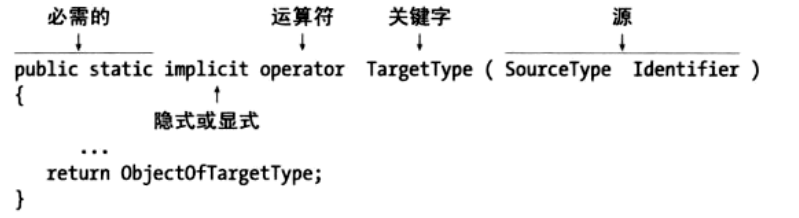
- 隐式转换用
implicit关键字 - 显示转换用
explicit关键字,转换时必须使用强制转换表达式。2.10.3.1. 自定义转换的约束
自定义类型转换有一些条件:
- 只能为class和struct定义类型转换
- 不能重定义标准隐式转换和显示转换
- 对于源类型S和目标类型T:
- S和T必须是不同的类型且S和T之间没有继承关系
- S和T不能是interface或者object类型
- 转换运算符必须是S或者T的成员。
2.10.3.2. 自定义类型转换示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace testConversion
{
class Person
{
public string Name;
public int Age;
public Person()
{
}
public Person(string name, int age)
{
Name = name;
Age = age;
}
//自定义隐式类型转换
public static implicit operator int(Person p)
{
return p.Age;
}
public static implicit operator Person(int age)
{
return new Person("Nemo", age);
}
}
class Employee : Person
{
}
class CustomConversion
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//int转Person
Person p = 10;
Console.WriteLine(p.Name);
Console.WriteLine(p.Age);
//Person转int
Person p1 = new Person("Tom", 23);
int age = p1;
Console.WriteLine(age);
//Employee继承自Person,Person可以转换到Int,int可以转换到float,
//所以Employee可以转换到float
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.Age = 23;
float fAge = emp;
Console.WriteLine(fAge);
}
}
}
2.10.4. is运算符
如果类型转换失败会抛出InvalidCastException异常,可以通过is运算符检查转换是否会成功,从而避免盲目尝试类型转换。
用法:Expr is TargetType,返回一个bool值
说明:当Expr可以通过引用转换、装箱、拆箱转换成目标类型,运算结果为true 示例:
Employee emp = new Employee();
Person p;
emp.Age = 23;
emp.Name = "Alice";
if (emp is Person)
{
p = emp;
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}\n年龄:{1}", p.Name, p.Age);
}
2.10.5. as运算符
as运算符和强制转换表达的作用一样,但在转换失败时返回null,而强制转换表达式会抛出转换异常。
as运算符只能用于引用转换和装箱转换,不能用于自定义转换或拆箱转换(引用类型到值类型)
示例:
//as运算符
Person p1 = emp as Person;
if (p1 != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("姓名:{0}\n年龄:{1}", p1.Name, p1.Age);
}
2.11. C#泛型
泛型:参数化的类型(type-parameterized),在编写类时不使用硬编码指定class的实际类型,而是使用占位符来表示,在创建泛型类的实例时才指定实际的class,以此让不同的class共享同一套代码,提高复用性和可扩展性。
2.11.1. 种类
C#提供了5种泛型:
- class
- struct
- 接口
- 委托
- 方法
泛型示例:
using System;
namespace testGeneric
{
class MyStack<T>
{
T[] StackArray;
const int MaxStack = 10;
int StackPointer = 0;
//属性
bool IsFull
{
get
{
return StackPointer >= MaxStack;
}
}
bool IsEmpty
{
get
{
return StackPointer <= 0;
}
}
//构造函数
public MyStack()
{
StackArray = new T[MaxStack];
}
//方法
public void Push(T t)
{
if (!IsFull)
{
StackArray[StackPointer++] = t;
}
}
public T Pop()
{
return (!IsEmpty) ? StackArray[--StackPointer] : StackArray[0];
}
public void Print()
{
for (int i = StackPointer-1; i >=0; i--)
{
Console.WriteLine("Value:{0}", StackArray[i]);
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyStack<int> stack = new MyStack<int>();
stack.Push(1);
stack.Push(2);
stack.Push(3);
stack.Push(4);
stack.Push(5);
stack.Print();
//
MyStack<string> strStack = new MyStack<string>();
strStack.Push("hello");
strStack.Push("Tom");
strStack.Push("nice");
strStack.Push("to");
strStack.Push("meet you");
strStack.Print();
}
}
}
运行结果:
Value:5
Value:4
Value:3
Value:2
Value:1
Value:meet you
Value:to
Value:nice
Value:Tom
Value:hello
2.11.2. 泛型参数类型约束
C#提供了约束泛型参数的手段,即约束泛型参数必须满足某些条件。
where子句用来描述泛型参数的条件,语法如下:
- 每一个有约束的参数有自己的where子句
- 如果参数有多个约束,使用逗号分隔
示例:
class MyClass<T1,T2,T3>
where T2:constraint,...
where T3:constraint,...
{
...
}
2.11.2.1. 约束类型和顺序
c#中的约束类型如下:
| 约束类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 类名 | 只有这种类或它的派生类型才能作为实参 |
| class | 任何引用类型都可以作为实参,包括类、数组、委托和接口 |
| struct | 任何struct都可以作为实参 |
| 接口名 | 只有这个接口或者实现它的类才能作为实参 |
| new() | 任何带有无参构造函数的类型都可作为实参,这叫做构造函数约束 |
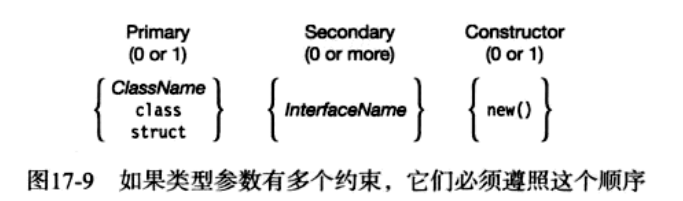
约束的顺序如下:
- 最多只能有一个主约束如果有则必须放在第一位
- 可以有任意多个接口名约束
- 如果有构造函数约束必须放在最后一位
2.11.3. 泛型方法
和其他泛型类型不同,泛型方法是成员,可以在泛型类、非泛型类、接口和struct中声明。
泛型方法有两个参数列表:类型参数列表和方法参数列表。
- 声明
public void Method<S,T>(S s,T t) where S:约束 { } - 调用 调用泛型方法:Method<short,int>(s,i),但编译器有时可以推断出实参的类型,这个时候在调用泛型方法时就不必再写出泛型类型,可以这样调用:Method(s,i);
2.11.4. 泛型委托
//泛型委托
delegate void MyDelegate<T>(T value);
delegate TR Func<T1, T2, TR>(T1 t1, T2 t2);
class Simple
{
public static void PrintString(string value)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
public static void PrintUpperString(string value)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}",value.ToUpper());
}
public static int Sum(int a,int b)
{
return a + b;
}
}
//使用泛型委托
//使用泛型委托
var myDel = new MyDelegate<string>(Simple.PrintString);
myDel += Simple.PrintUpperString;
myDel("hello,Tom!");
var func = new Func<int,int,int>(Simple.Sum);
Console.WriteLine("{0}", func(15, 16));
- 应用 C#的LINQ特性在很多地方使用了泛型委托
2.12. LINQ
LINQ,全称Language Intergrated Query
2.13. 命名空间
使用命名空间是管理类的一种手段,命名空间可以在不同的文件中扩展以添加更多的类,命名空间也可以嵌套,主要有两种方式:
- 原文嵌套
namespace Corp{ namespace Tech{ } } - 分离的声明
namespace Corp{ } namespace Corp.Tech{ }这两种嵌套的方式都生成相同的程序集。
2.13.1. using
如果在程序中使用一个类,使用完全限定名非常冗长,可以在源文件开头使用using指令引入命名空间,using指令通知编译器将要使用某个命名空间下的类,然后就可以使用简单类名了。
using允许给命名空间和命名空间中的类起别名,如:
//定义别名
using Sys = System;
using SC = System.Console;
//使用别名
SC.WriteLine("using让SC作为Console别名");
Sys.Console.ReadKey();
2.13.2. 程序集标识符
程序集标识符分为4个部分,可以唯一标识该程序集:
- 简单名
- 版本号:3个
.分开的一串数字 - 文化:如en-Us,de-DE
- 公钥:128个字节大小的字符串
2.14. 异常
异常是指程序运行过程中出现的错误,当异常发生时,CLR会创建异常对象并寻找catch块进行处理,BCL定义了很多异常类,所有的异常类都派生自System.Exception。
.Net中的异常继承体系如下:
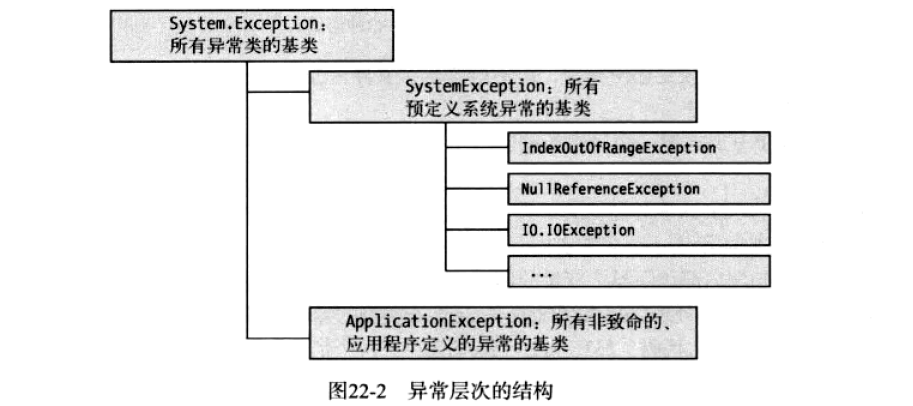
异常对象含有只读属性,包括:
- Message:解释异常原因的消息
- StackTrace:描述异常发生在何处
- InnerException:由哪一个异常引发,是前一个异常的引用
- HelpLink:为异常信息提供URN和URL
- Source:如果没有被应用程序定义的异常设定,那么这个属性含有异常所在的程序集名称。
2.14.1. catch子句
catch子句处理异常,有3种形式,允许不同级别的处理:
- 一般catch子句
catch { Statements }性质:
- 在
catch后没有参数列表 - 可以匹配try块中抛出的任何类型异常
- 在
- 特定catch子句
catch(ExceptionType) { Statements }性质:
catch后只有异常参数类型,没有标识符- 匹配该类型任何异常
- 带对象的catch子句 特定的catch子句+异常对象标识符,用于需要访问异常对象获取该对象信息的场景。
2.14.2. finally代码块
finally中的代码一定会执行,即使try中有return语句。
值得一提的是,C#的finally语句块中不允许含有return语句,这和Java是不同的。
2.14.3. 抛出异常
可以用throw语句显式抛出一个异常,语法如下:
throw ExceptionObject;
2.15. 预处理指令
2.16. 反射和特性(Attribute)
BCL声明了一个抽象类Type,它被设计用来包含类的特性
,使用Type的对象可以让我们获取程序中使用的类的信息。
由于Type是一个抽象类,不能直接创建它的实例,在我们获取Type类型的实例时CLR返回的是派生类的实例。
对于Type需要了解的是:
- 对于程序中使用到的每个类,CLR都会创建一个包含类型信息的Type类型的实例
- 每个类型都会关联到一个独立的Type对象
- 不管一个类型有多少个实例,它对应的Type对象实例始终只有一个
2.16.1. 获取Type对象
获取Type对象引用的方式有2种:
- 调用
GetType()方法,此方法在object类中定义,因此所有实例都可以调用 - 使用
typeof运算符,使用typeof(类名)获取Type对象引用
示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
namespace testReflectionAndAttribute
{
class BaseClass
{
public int BaseField;
}
class DerivedClass : BaseClass
{
public int DerivedField;
}
class TypeTest1
{
public void Run()
{
BaseClass bc = new BaseClass();
DerivedClass dc = new DerivedClass();
BaseClass[] classes = new BaseClass[]{ bc, dc };
foreach ( var instance in classes)
{
Type t=instance.GetType();
Console.WriteLine("类型:" +t.Name);
FieldInfo[] fs=t.GetFields();
foreach (var f in fs)
{
Console.WriteLine("\t字段:" + f.Name);
}
}
}
}
}
2.16.2. 特性(Attribute)
C#中的特性(Attribute)跟Java中的注解(Annotation)功能相似。
Attribute的目的:告诉编译器把程序结构的某组元数据嵌入程序集。
特性片段用方括号[]包围,其中是特性的名称和参数列表
2.16.2.1. dotNET预定义特性
- Obsolete
标记方法已经过期,不推荐使用
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace testReflectionAndAttribute { class AttributeTest { public void Run() { ObsoleteMethod(); //ErrorMethod(); } [Obsolete("此方法已经弃用")] public void ObsoleteMethod() { Console.WriteLine("此方法已经弃用!"); } //第二个参数为true代表禁止调用这个过时的方法,会产生编译错误 [Obsolete("此方法已经弃用",true)] public void ErrorMethod() { Console.WriteLine("此方法已经弃用!"); } } } - Conditional
//定义DoTrace,则TraceMessage会被正常调用,否则所有这个方法的调用都会被忽视。 #define DoTrace using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Text; namespace testReflectionAndAttribute { class AttributeTest2 { public void Run() { TraceMessage("Start of Run()"); Console.WriteLine("doing in Run()"); TraceMessage("End of Run()"); } //Conditional特性 [Conditional("DoTrace")] public void TraceMessage(string str) { Console.WriteLine(str); } } } -
调用者信息特性 调用者信息特性有3个,分别是CallerFilePath、CallerLineNumber和CallerMemberName。
注意:这些特性只能用于方法中的可选参数
//定义DoTrace,则TraceMessage会被正常调用,否则所有这个方法的调用都会被忽视。 #define DoTrace using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; using System.Text; namespace testReflectionAndAttribute { /** * 调用者特性 */ class AttributeTest3 { public void Run() { //CallerFilePath //CallerLineNumber //CallerMemberName MyTrace("Hello,C#"); } public void MyTrace(string msg, [CallerFilePath] string filePath="", [CallerLineNumber]int lineNumber=0, [CallerMemberName]string memberName="" ) { Console.WriteLine("file path:{0}",filePath); Console.WriteLine("line number:{0}", lineNumber); Console.WriteLine("called from:{0}", memberName); Console.WriteLine("Message:{0}",msg); } } }运行结果:
file path:C:\Users\SKQ\source\repos\testReflectionAndAttribute\testReflectionAndAttribute\AttributeTest3.cs line number:25 called from:Run Message:Hello,C# -
DebuggerStepThrough特性
[DebuggerStepThroung]可作用于类、struct、构造函数、方法或访问器,这个特性告诉调试器在调试时跳过这些部分的调试。 - 其他特性
2.16.2.2. csharp特性目标
c#定义了10种特性目标:
- event
- method
- property
- type
- assembly
- field
- param
- return
- typevar
- module
2.16.2.3. 自定义特性
有关特性的要点如下:
- 特性不是新的数据结构,而是class类型
- 所有的特性都派生自
System.Attribute - 特性在定义时必须以
Attribute结尾,使用时使用短名称
2.16.2.3.1. 特性的constructor
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
namespace testReflectionAndAttribute
{
class MyAttribute : Attribute
{
public MyAttribute()
{
}
public MyAttribute(string s1,bool flag)
{
}
}
[My]
class AttributeTest5
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Run...");
}
}
}
2.16.2.3.2. 特性构造方法参数
可以有位置参数和命名参数
2.16.2.4. 限制特性的使用
特性[AttributeUsage]可以限制特性的用法,比如限制特性只能应用在方法上。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
namespace testReflectionAndAttribute
{
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Field)]
class MyAttribute : Attribute
{
public MyAttribute()
{
}
public MyAttribute(string s1,bool flag)
{
}
}
//[My]
//这里会编译错误,因为AttributeUsage限制了使用
class AttributeTest5
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Run...");
}
}
}
AttributeUsageAttribute特性有三个属性:ValidOn、AllowMultiple和Inherited,ValidOn是AttributeTargets枚举类型,指定特性的应用范围,Inherited是bool值,默认为true,指示应用特性的类的派生类是否可以继承特性;AllowMultiple是bool值。
2.16.2.5. 获取特性
通过GetCustomAttributes()方法获取应用在目标上的特性集合:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
namespace testReflectionAndAttribute
{
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class)]
class MyClassAttribute : Attribute
{
public string Description { get; set; }
public string VisionNumber { get; set; }
public string ReviewerId { get; set; }
public MyClassAttribute(string desc,string ver)
{
Description = desc;
VisionNumber = ver;
}
}
//[My]
//这里会编译错误,因为AttributeUsage限制了使用
[MyClass("这个类用来测试获取自定义的特性","1.0.0")]
class AttributeTest6
{
public void Run()
{
Type t=this.GetType();
object[] attributes= t.GetCustomAttributes(false);
foreach (var attr in attributes)
{
MyClassAttribute myAttr = attr as MyClassAttribute;
Console.WriteLine("Description:{0}", myAttr.Description);
Console.WriteLine("VisionNumber:{0}", myAttr.VisionNumber);
Console.WriteLine("ReviewerID:{0}",myAttr.ReviewerId);
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
Description:这个类用来测试获取自定义的特性
VisionNumber:1.0.0
ReviewerID:
2.16.2.6. IsDefined
IsDefined方法可以判断某个Attribute是否应用在了某个结构上:
[MyClass2("这个类用来测试获取自定义的特性","1.0.0")]
class AttributeTest7
{
public void Run()
{
Type t=this.GetType();
bool isDefined=t.IsDefined(typeof(MyClass2Attribute), false);
if (isDefined)
{
Console.WriteLine("MyClass2Attribute被应用到了AttributeTest7上");
}
}
}
2.17. 其他主题
2.17.1. 可空类型
可空类型允许把一个值类型的变量标记为有效或无效,可以把null值赋给值类型。
可以从任何值类型创建可空类型,可空类型的形式为类型? 变量名
示例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace testOther
{
class NullableTypeTest
{
public static void Test()
{
int? a = 10;
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.WriteLine(a.GetType());
a = null;
//可空类型转换成不可空必须强制转换
if (a != null)
{
int b = (int)a;
Console.WriteLine(b);
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
10
System.Int32
2.17.1.1. 可空类型的可访问性和本质
对于可空类型,不会直接暴露类型的成员,只能通过Value属性访问
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace testOther
{
class NullableTypeTest
{
public static void Test()
{
int? a = 10;
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.WriteLine(a.GetType());
a = null;
//可空类型转换成不可空必须强制转换
if (a != null)
{
int b = (int)a;
Console.WriteLine(b);
}
MyStruct myStruct1 = new MyStruct(1, 2);
MyStruct? myStruct2 = new MyStruct(3, 4);
//和上面的作用完全相同
Nullable<MyStruct> nMyStruct = new Nullable<MyStruct>(new MyStruct(10,10));
//可空类型只能通过Value属性来访问成员
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", myStruct1.X, myStruct1.Y);
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", myStruct2.Value.X, myStruct2.Value.Y);
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", nMyStruct.Value.X, nMyStruct.Value.Y);
}
struct MyStruct
{
public int X;
public int Y;
public MyStruct(int x,int y)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
10
System.Int32
1,2
3,4
10,10
可空类型的本质:
可空类型通过System.Nullable<T>来实现,可空语法的问号语法是创建Nullable<T>类型实例的快捷语法。