1. 基础语法
1.1. 访问权限
Java中一共有四种权限,其中有3个权限修饰关键字。权限修饰关键字用来修饰class、method和field。 对于不同修饰符修饰的成员方法和成员变量,不同情况访问权限不同。
| 关键字 | 权限 |
|---|---|
| private | 只有当前类的方法可以访问 |
| 默认(无关键字) | 包括上一种情况,同package下的类都可访问 |
| protected | 上面两种情况都可访问,不同package的子类可访问 |
| public | 任意package的任意类都可访问 |
1.2. 多态(polymorphic)
polymorphic,意思是have many forms,即有多种形态,更具体地说,一个对象在不同时刻体现出不同的形态。
1.2.1. 前提条件
- 有继承关系
- 子类重写父类的方法
- 父类引用指向子类对象
1.3. super与this
- 子类实例创建时会创建一个父类对象吗? 不会,只是在子类对象内存区域有一块是存放父类继承过来的字段。
- super指向的是父类对象的引用吗?
不是,super只是用来访问父类的字段和方法,它不指向具体的对象,因为创建子类对象时父类对象不会创建。
package com.huangbei; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { new Son().showClass(); } } class Father{ } class Son extends Father{ public void showClass(){ System.out.println(super.getClass()); System.out.println(this.getClass()); } }输出结果:
class com.huangbei.Son class com.huangbei.Son
2. I/O流
Java中所有的输入输出都是以stream的形式操作的,Java I/O体系如下:
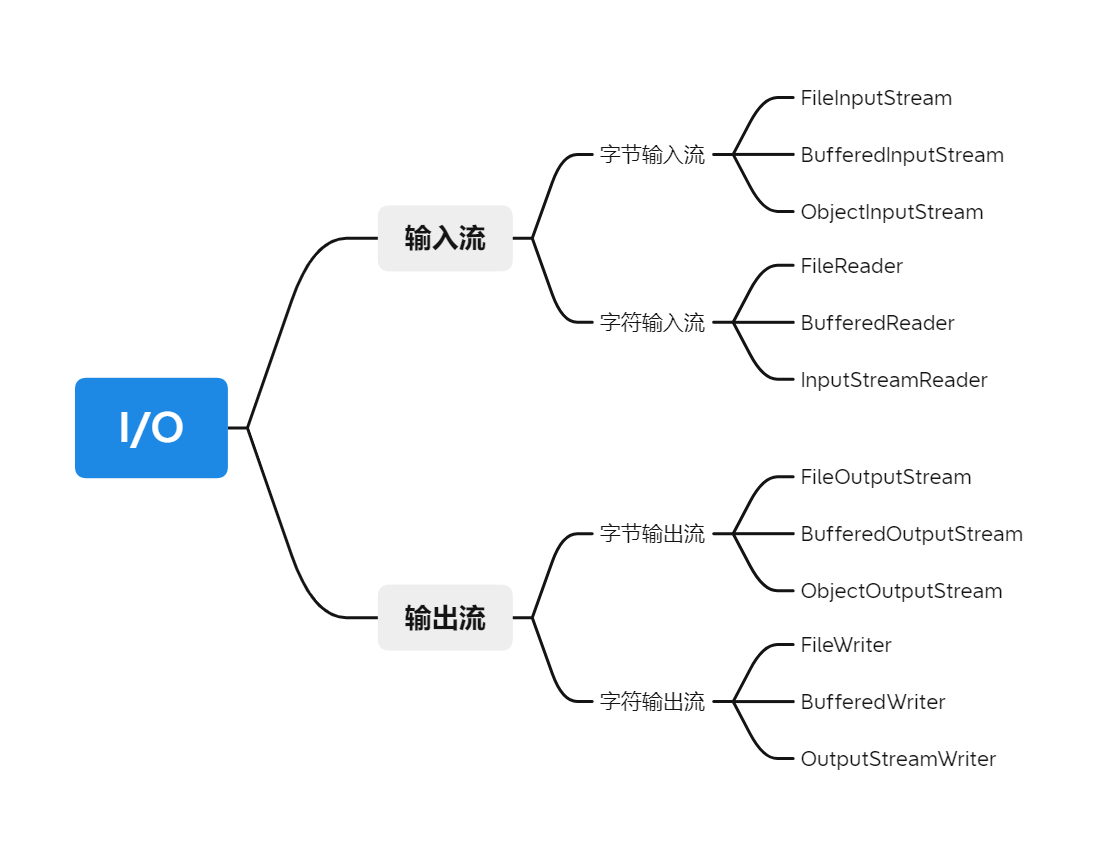
2.1. 字节流
2.1.1. 字节输入流
InputStream这个抽象类是表示输入字节流的所有类的超类。
2.1.1.1. FileInputStream
public class FileInputStream extends InputStream
它的方法包括:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int available() | 从下一次调用此输入流的方法返回可从该输入流读取(或跳过)的字节数,而不会阻塞。 |
| void close() | 关闭此输入流并释放与流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
| void mark(int readlimit) | 标记此输入流中的当前位置。 |
| boolean markSupported() | 测试此输入流是否支持 mark和 reset方法。 |
| abstract int read() | 从输入流读取数据的下一个字节。 |
| int read(byte[] b) | 从输入流中读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到缓冲器阵列 b 。 |
| int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 从输入流读取最多 len个字节的数据到字节数组。 |
| byte[] readAllBytes() | 从输入流读取所有剩余字节。 |
| int readNBytes(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 将所请求的字节数从输入流读入给定的字节数组。 |
| void reset() | 将此流重新定位到最后在此输入流上调用 mark方法时的位置。 |
| long skip(long n) | 跳过并丢弃来自此输入流的 n字节的数据。 |
| long transferTo(OutputStream out) | 从该输入流中读取所有字节,并按读取的顺序将字节写入给定的输出流。 |
文件字节
2.1.1.2. BufferedInputStream
继承关系:
java.lang.Object
java.io.InputStream
ava.io.FilterInputStream
java.io.BufferedInputStream
不同于FileInputStream,BufferedInputStream不是直接继承自InputStream抽象类。
BufferedInputStream对流的操作实际上是通过FileInputStream来完成的,但BufferedInputStream内置了缓冲区功能,外部调用BufferedInputStream的read()时实际上是从缓冲区读取,大大减少了磁盘IO的次数,提高了读取速度。
2.1.2. 字节输出流
OutputStream是一个抽象类,是Java中所有输出流的超类,输出流将字节发送到某个接收器,它里面定义的方法包括:
| 修饰符和返回值 | 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| void | close() | 关闭此输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。 |
| void | flush() | 刷新此输出流并强制任何缓冲的输出字节被写出。 |
| void | write(byte[] b) | 将 b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流。 |
| void | write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 从指定的字节数组写入 len字节,从偏移量 off开始输出到此输出流。 |
| abstract | void write(int b) | 将指定的字节写入此输出流。 |
2.1.2.1. FileOutputStream
public class FileOutputStream extends OutputStream
文件字节输出流,针对文件进行操作且只能进行字节输出操作。
示例:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestFileOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("output.txt",true);
){
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
fos.write("hello,world!".getBytes());
fos.write("\n".getBytes());
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.1.2.2. 案例:字节流复制文件
注意:在使用字节输出流输出到目标文件时,不要使用write(byte[] bytes)方法,否则在读取到文件末尾时bytes数组的内容长度可能比数组的length要小,导致最后会有一部分多余的数据被写入,OutputStream写入文件一定要注意写入的字节个数len。
import java.io.*;
public class TestFileInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("output.txt");
) {
// copyByByte(fis,fos);
copyByBytes(fis,fos);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 不使用缓冲区复制
* @param is
* @param os
*/
private static void copyByByte(InputStream is, OutputStream os) throws IOException {
int data;
while ((data=is.read())!=-1){
os.write(data);
}
}
/**
* 使用缓冲区复制
* @param is
* @param os
*/
private static void copyByBytes(InputStream is, OutputStream os) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(bytes))!=-1){
os.write(bytes,0,len);
}
}
}
2.1.2.3. 案例:复制文件夹
import java.io.*;
/*
给定一个源文件夹,将其复制到E:盘根目录下
*/
public class CopyDirectory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File src = new File("E:\\");
// System.out.println(srcDir.getName());
File dest = new File("E:\\temp");
copy(src,dest);
}
private static void copy(File src, File dest) {
if(src.isFile()){
//src是一个文件
copyFile(src,new File(dest,src.getName()));
}else {
//src是一个目录
//新建目标目录
File newFolder = new File(dest, src.getName());
if(!newFolder.exists()){
newFolder.mkdirs();
}
File[] files = src.listFiles();
for(File f:files){
copy(f,newFolder);
}
}
}
private static void copyFile(File srcFile, File destFile) {
try (
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));
) {
byte[] bytes=new byte[2048];
int len;
while ((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.1.2.4. BufferedOutputStream
跟BufferedInputStream类似,这个类是带缓冲区功能的字节输出流。
2.2. 字符流
2.2.1. 字符输入流
java.io包下,字符输入流相关的继承关系图如下:

字符输入流的构造依赖于字节输入流,字符输入流只是以特定的字符集对字节输入流进行解码并以流的方式提供给使用者操作。
-
public abstract class Reader extends Object用于读取字符流的抽象类,定义的方法有:方法 描述 abstract void close() 关闭流并释放与之相关联的任何系统资源。 void mark(int readAheadLimit) 标记流中的当前位置。 boolean markSupported() 告诉这个流是否支持mark()操作。 int read() 读一个字符 int read(char[] cbuf) 将字符读入数组。 abstract int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) 将字符读入数组的一部分。 int read(CharBuffer target) 尝试将字符读入指定的字符缓冲区。 boolean ready() 告诉这个流是否准备好被读取。 void reset() 重置流。 long skip(long n) 跳过字符 -
InputStreamReader public class InputStreamReader extends Reader InputStreamReader是从字节流到字符流的桥梁:它读取字节,并使用指定的charset将其解码为字符。 它使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者可以接受平台的默认字符集。
每个调用InputStreamReader的read()方法之一可能会导致从底层字节输入流读取一个或多个字节。 -
FileReader public class FileReader extends InputStreamReader 阅读字符文件的便利的class。 该类的构造函数假定默认字符编码和默认字节缓冲区大小是适当的。 要自己指定这些值,请在FileInputStream上构造一个InputStreamReader。
FileReader用于读取字符流。 要读取原始字节流,请考虑使用FileInputStream 。 -
BufferedReader public class BufferedReader extends Reader 从字符输入流读取文本,缓冲字符,以提供字符,数组和行的高效读取。可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以使用默认大小。 默认值足够大,可用于大多数用途。 对于OutputStreamReader和FileReader,每一次read()操作都会导致底层IO,效率低下,因此用BufferedReader将他们包装,可增加缓冲功能,以大大提高效率。
2.2.2. 字符输出流
2.2.2.1. 案例:编码转换
package com.huangbei.io.input;
import java.io.*;
public class TestInputStreamReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// gb2312编码的txt转utf-8
try (
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("斗破苍穹.txt");
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis,"gb2312");
OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("斗破苍穹(copy).txt"),"utf-8");
) {
char[] chars = new char[2048];
int len;
while ((len=isr.read(chars))!=-1){
osw.write(chars,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.3. 对象序列化流
jdk内置了ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream是专门用来序列化对象的字节流类。这两个类分别继承自InputStream和OutputStream。
除了jdk内置的对象序列化机制,还有很多第三方的对象序列化实现且比jdk内置的要优秀。
2.3.1. 对象序列化的使用场景
- 对象持久化到文件,比如tomcat对session对象有持久化机制。
- 对象在网络上传输,比如分布式系统中的远程方法调用。
案例:对象持久化到文件
package com.huangbei.io.output;
import javafx.beans.binding.ObjectExpression;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TestObjectStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// write();
read();
}
private static void write() throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("object.data"));
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("乔峰", 40));
list.add(new Student("段誉", 25));
list.add(new Student("虚竹", 27));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(list);
}
private static void read() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("object.data"));
Object o = objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println(o);
}
}
class Student implements Serializable{
static final long serialVersionUID=7102412401203991L;
private String name;
private int age;
private transient int id;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
}
注意
- 需要序列化的类必须实现Serializable接口
- 强烈建议为类的成员显示声明一个
static final long serialVersionUID,且尽可能使用private修饰 - 如果不想某个成员被序列化过程忽略,使用
transient修饰。