1. 线程安全集合
1.1. 1.jdk遗留
- HashTable<K,V>
- Vector
1.2. 2.Collections方法扩展
- public static
List synchronizedList(List list) - public static <K,V> Map<K,V> synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m)
- ……
- ……
Collections中的这些方法只是对参数的方法进行包装,使用synchronized和一个Object类型的mutex来实现多线程互斥访问,本质还是synchronized锁。
1.3. 3.juc包下的的线程安全集合(本文重点讨论)
1.3.1. ConcurrentHashMap
1.3.1.1. 使用例子
package com.huangbei.test3;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Test1 {
static String ALPHA = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.将26个字母填充200次到一个list中
ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
int count = 200;
for (int i = 0; i < ALPHA.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < count; j++) {
words.add(String.valueOf(ALPHA.charAt(i)));
}
}
//2.将list洗牌
Collections.shuffle(words);
//3.将list分成26个sublist并在每个sublist中的字母之间插入\n,然后将sublist分别写入26个文件
for (int i = 0; i < ALPHA.length(); i++) {
try {
String filePath = "data/";
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
String fileName = filePath + (i + 1) + ".txt";
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(fileName);
String collect = words.subList(i * count, (i + 1) * count).stream().collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
fw.write(collect);
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//4.读取所有的文件,统计字母的个数并打印
demo(
() -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>(),
(map, list) -> {
for (String word : list) {
Integer n = map.get(word);
map.put(word, n == null ? 1 : n + 1);
}
}
);
}
private static void demo(Supplier<Map<String, Integer>> supplier, BiConsumer<Map<String, Integer>, List<String>> biConsumer) {
Map<String, Integer> map = supplier.get();
//26个线程,分别读取26个文件,每个文件的内容用List接收,对list使用consumer统计
ArrayList<Thread> threads = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) {
String filename = "data/" + i + ".txt";
threads.add(
new Thread(() -> {
List<String> words = readFile(filename);
biConsumer.accept(map, words);
})
);
}
threads.forEach(Thread::start);
threads.forEach(t -> {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println("统计结果:\n" + map);
}
private static List<String> readFile(String filename) {
ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(filename);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String str;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
words.add(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return words;
}
}
结果:
统计结果:
{a=193, b=200, c=200, d=200, e=199, f=199, g=199, h=199, i=198, j=200, k=199, l=198, m=199, n=200, o=199, p=200, q=200, r=200, s=200, t=200, u=199, v=200, w=200, x=199, y=199, z=199}
注意:ConcurrentHashMap只能保证单个方法是并发安全的,但是不能保证方法的组合是并发安全的,在上面的例子中,尽管使用了ConcurrentHashMap作为集合容器,但结果还是产生了线程安全问题。
1.3.1.1.1. 解决方法
使用LongAdder作为value,用来计数。
配合computeIfAbsent()使用
(map,list)->{
for (String word : list) {
LongAdder adder = map.computeIfAbsent(word, (key) -> new LongAdder());
adder.increment();
}
}
computeIfAbsent(K key,Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction):如果key在map中不存在,使用mappingFunction进行计算,将计算结果和key存入map并返回计算结果。
1.3.1.2. 原理
1.3.1.2.1. get(Object key)
get()方法保证线程安全的原因是因为Node节点的value和next都使用了volatile关键字修饰,保证线程对这两个值的修改对其他线程可见。
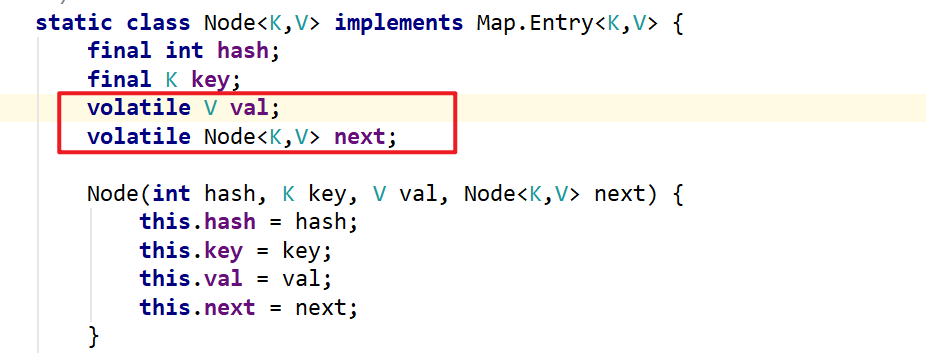
1.3.1.2.2. put()
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
//对链表头结点加锁
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
//遍历链表
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
//更新value
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
//没有找到key,追加新节点设置key,value
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
//树化节点
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
//链表节点数量超过树化阈值,将table[i]的链表树化
//但超过阈值首先是扩容,等到table.length达到64,再开始树化。
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
1.3.1.3. 线程安全类的操作在程序中不一定线程安全
谨记:安全地使用线程安全类。
比如这么一段代码:
private static ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Object> hashMap;
public static void putIfAbsent(int key, Function<Integer, Object> callback) {
if (!hashMap.contains(key)) {
hashMap.put(key, callback.apply(key));
}
}
ConcurrentHashMap的contains操作和put操作都是线程安全的,但是这个putIfAbsent就不是线程安全的操作。比如线程A和线程B,都检测到hashMap中没有当前这个key,然后都进行put操作,就会出现线程A put之后,线程B 再put了一次,将线程A的put结果覆盖了。在线程A看来,callback执行了,但是hashMap中的值却不对。这个现象,轻则导致单例对象重复创建,影响性能;重则导致影响业务数据,比如hashMap中存储的是用户的登记信息,callback是扣款操作,那么影响就很严重。
作者:RobertLu
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/366463446/answer/982204638
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。