1. 再谈ReentrantLock
1.1. 继承关系
ReentrantLock是基于AQS,它里面使用的同步器Sync是继承自AQS,另外里面还有两个同步器都是继承自这个Sync:FairSync和NonfairSync。
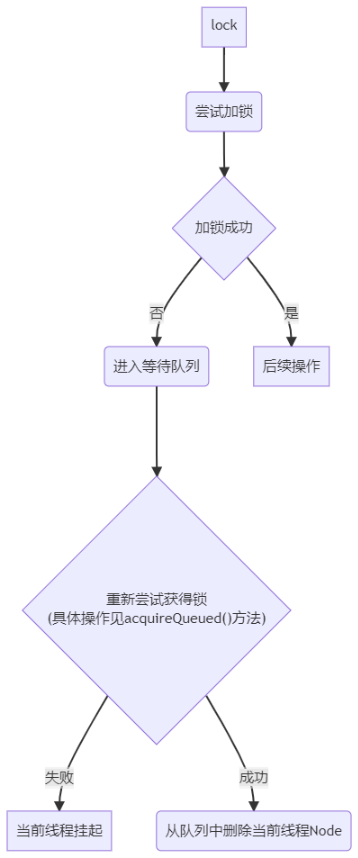
1.2. 加锁流程
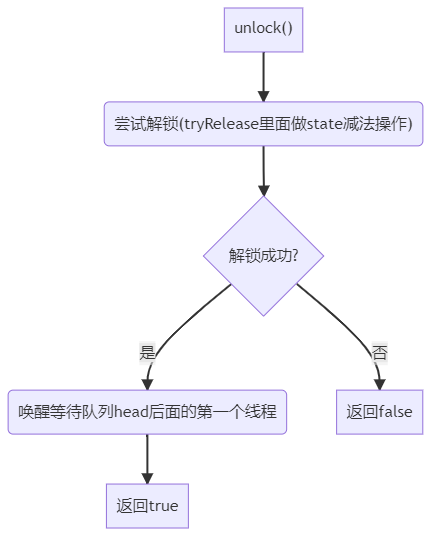
1.3. 解锁流程
1.4. 可重入原理
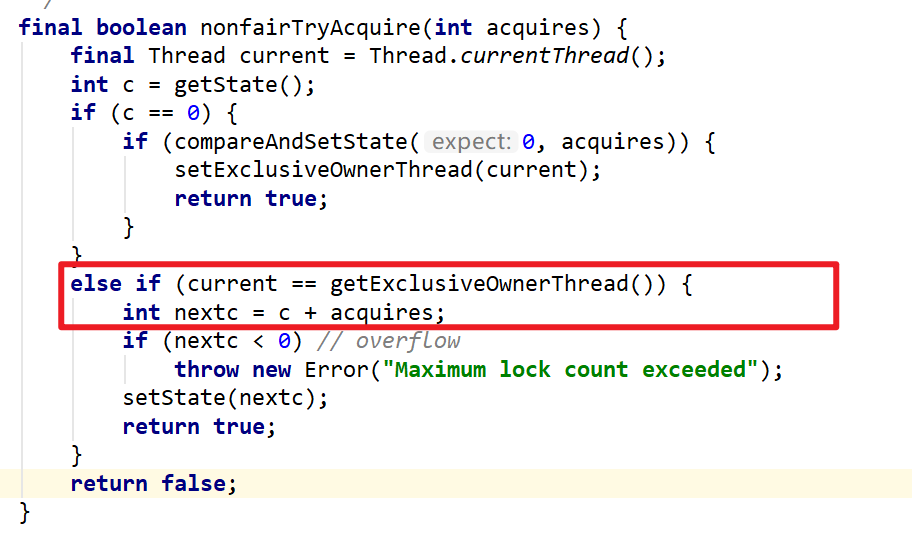 在拥有锁的线程尝试重入时,ReentrantLock对重入机制的实现是将Sync的state++。
在拥有锁的线程尝试重入时,ReentrantLock对重入机制的实现是将Sync的state++。
1.5. 可打断原理(AQS)
可打断和不打断是AQS设计和实现的,ReentrantLock提供lock()和lockInterruptibly()来完成不可中断加锁和可中断加锁,实际调用的是AQS的aqcuire()和acquireInterruptibly()。
-
不可打断模式:如果线程在获取锁的过程中被interrupt,不会停止获取锁,直到它获取到锁才能知道自己被打断过(interrupted为true)。
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true; try { boolean interrupted = false; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); //如果线程执行了parkAndCheckInterrupt()即调用了park(this),会被挂起 //如果在这之间线程被interrupt(),parkAndCheckInterrupt()会返回打断标记(true)并清除 //如果下次循环线程tryAcquire()返回true即拿到锁,会返回interrupted,否则继续挂起 //这意味着如果线程在park()时被interrupt,只有线程拿到锁才会知道自己被打断过。 if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } } -
可打断模式:如果线程在加锁过程中被调用interrupt(),会直接抛出异常。
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException { //这里可能抛出异常 if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException(); if (!tryAcquire(arg)) doAcquireInterruptibly(arg); } private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException { final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE); boolean failed = true; try { for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return; } //这里可能抛出异常 if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) throw new InterruptedException(); } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
1.6. 公平锁和非公平锁原理
1.6.1. 非公平锁
直接对state变量进行CAS操作
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
//如果state为0,直接CAS操作。
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
1.6.2. 公平锁
先检查Sync的等待队列中当前线程是否是第一个等待的或者等待队列是否为空,如果不是,尝试加锁失败,返回false,如果是,再进行CAS操作。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
//如果state为0
//先判断当前线程在等待队列是否排第一或者等待队列是否为空,即调用hasQueuedPredecessors()判断
//如果是,进行CAS操作;否则tryAcquire()返回false
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
1.7. 条件等待/唤醒原理
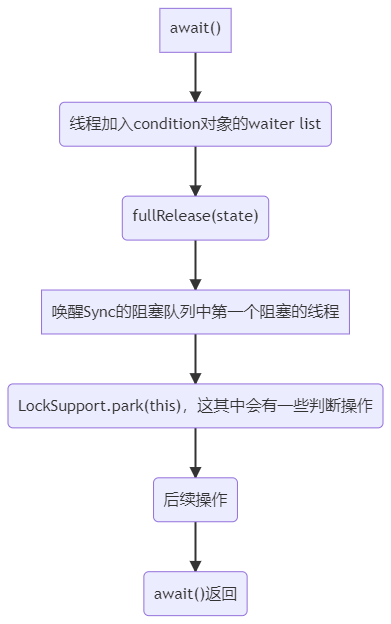
1.7.1. 1.await()
Condition对象在执行await()时要先释放锁并唤醒Sync阻塞队列中的第一个线程。
1.7.2. 2.signal()
signal()是将condition的等待链表的第一个结点转移到Sync的阻塞队列中。
/**
* Moves the longest-waiting thread, if one exists, from the
* wait queue for this condition to the wait queue for the
* owning lock.
*
* @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if {@link #isHeldExclusively}
* returns {@code false}
*/
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);
}
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)
lastWaiter = null;
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) &&
(first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
/**
* Transfers a node from a condition queue onto sync queue.
* Returns true if successful.
* @param node the node
* @return true if successfully transferred (else the node was
* cancelled before signal)
*/
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.
*/
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
/*
* Splice onto queue and try to set waitStatus of predecessor to
* indicate that thread is (probably) waiting. If cancelled or
* attempt to set waitStatus fails, wake up to resync (in which
* case the waitStatus can be transiently and harmlessly wrong).
*/
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
return true;
}